Enhancing Energy Efficiency in South Africa: Insights into Emission Scopes and Smart Solutions
Introduction
In today’s eco-conscious market, understanding and implementing strategies for energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emission reductions are crucial for sustainable development. South Africa, with its unique energy profile heavily reliant on coal, faces significant challenges and opportunities in transitioning towards a more sustainable energy landscape. This post explores the essential categories of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, delves into the specifics of energy consumption across various sectors, and introduces an innovative solution from Smart-View Technology to optimize utility management.
Understanding Emission Scopes and Their Impact:
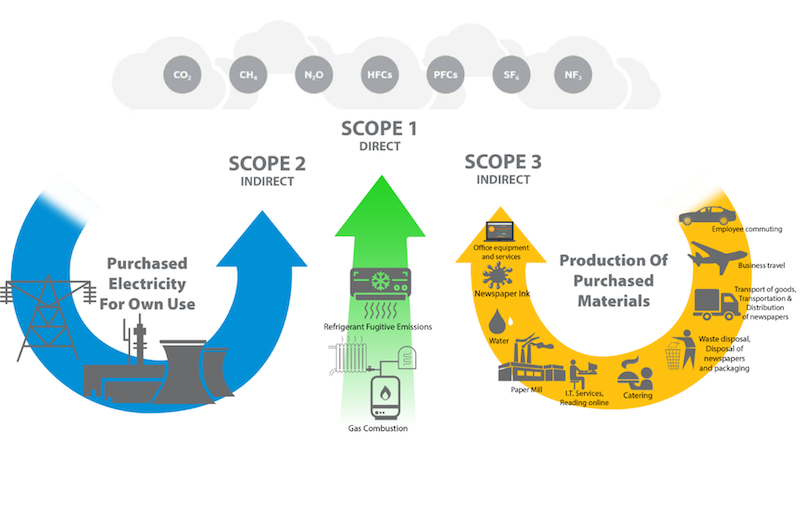
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are categorized into three scopes by the GHG Protocol, which helps in managing and reporting emissions:
Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources.
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling.
Scope 3: All other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain.
Addressing these emissions is vital for companies aiming to reduce their environmental footprint and comply with global sustainability standards.
South Africa’s Energy Consumption by Sector and Subsector:
South Africa’s energy consumption paints a complex picture, intricately woven with the demands of various sectors and subsectors. This vibrant tapestry not only reflects the nation’s economic activities but also mirrors its societal needs and environmental challenges.
In the industrial sector, energy serves as the lifeblood powering manufacturing, mining, and construction activities. Here, heavy machinery and high-energy processes drive demand, making efficiency paramount. Subsectors like steel, chemicals, and automotive manufacturing exhibit unique energy profiles, each demanding tailored solutions for sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
| Sector | Energy Consumption (%) | Subsector | Energy Consumption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | 51 | Chemical and Petrochemical | 28 |
| Iron and Steel | 13 | ||
| Non-Ferrous Metals | 7 | ||
| Non-Metallic Minerals | 3 | ||
| Mining and Quarrying | 10 | ||
| Food and Tobacco | 1 | ||
| Pulp and Paper | 1 | ||
| Others | 37 | ||
| Transport | 26 | Road Transport | 78 |
| International Civil Aviation | 10 | ||
| Domestic Air Transport | 10 | ||
| Others | 2 | ||
| Agricultural | 2 | Mainly liquid fuels used for transportation of goods | N/A |
| Residential | 7 | Electricity | 76 |
| Renewables | 12 | ||
| Geothermal | 7 | ||
| Coal | 5 | ||
| Commerce and Public Services | 11 | Financial services, IT, Retail, Tourism, Government and quasi government institutions | N/A |
This data underscores the critical areas where energy efficiency initiatives could yield significant benefits.
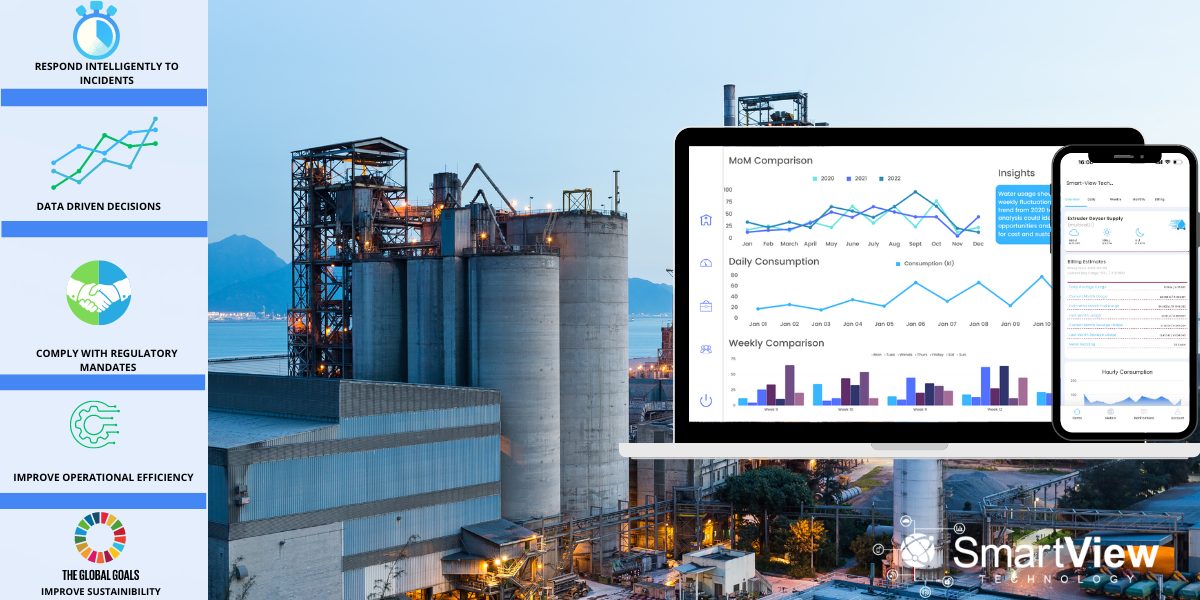
Smart-View Technology: A Utility Management Solution:
In response to the urgent need for efficient energy management, Smart-View Technology offers a comprehensive utility management solution tailored to South African businesses and industries. This system enables organizations to monitor and control their energy usage effectively, helping to reduce costs and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The technology provides real-time data analytics, allowing for proactive management of energy resources across various sectors, from industrial to residential.
Moreover, Smart-View fosters a culture of accountability and sustainability. By promoting transparency and awareness of resource usage, it encourages individuals and organizations to adopt more eco-conscious behaviors. This not only benefits the bottom line but also contributes to broader environmental conservation efforts.
In essence, Smart-View Technology transcends mere utility management; it represents a paradigm shift towards smarter, more sustainable living. By harnessing the power of data and connectivity, it paves the way for a future where efficiency and environmental responsibility go hand in hand.
Conclusion
Embracing energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions are imperative for South Africa’s sustainable future. By understanding the different scopes of emissions and analyzing energy consumption by sector, businesses can implement more targeted strategies. Solutions like the utility management system from Smart-View Technology not only offer substantial energy savings but also contribute to the global effort against climate change. Let’s commit to a greener, more efficient tomorrow..



